|
The more negative 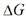 for ATP hydrolysis derives primarily from its more exothermic nature
(neg.
for ATP hydrolysis derives primarily from its more exothermic nature
(neg.  ).
The greater exothermicity associated with ATP hydrolysis is a consequence
of the smaller input of energy (enthalpy) required to rupture the
weaker phosphoanhydride linkage in comparison with the phosphodiester
link in DNA: ).
The greater exothermicity associated with ATP hydrolysis is a consequence
of the smaller input of energy (enthalpy) required to rupture the
weaker phosphoanhydride linkage in comparison with the phosphodiester
link in DNA:
|
|
 (hydrolysis) (hydrolysis)
(kJ/mol)
|
|
ATP + H2O --> ADP + Pi
|
-24.2
|
|
DNA + H2O --> 5’DNA + 3’DNA
|
-12.0
|
so that reversing the 2nd reaction in the direction of DNA formation:
|
ATP + H2O --> ADP + Pi
|
-24.2
|
|
5’DNA + 3’DNA --> DNA + H2O
|
12.0
|
results in an overall exothermic process if the condensation of
the 2 DNA fragments can be coupled to the ATP hydrolysis reaction:
|
5’DNA + 3’DNA + ATP --> DNA + ADP + Pi
|
-11.8
|
|

